

The Government of Uttar Pradesh (GoUP) is proactively working towards designing innovative health systems, and a critical aspect has been the availability of quality health data. A robust data system can help in capturing and generating a wide range of quality health data that can be used for public health sector decision-making and can improve health outcomes basis the data-based treatment decisions, digital therapeutics, clinical trials, self-management of care and person-centred care.
A large number of health programs are operational under the National Health Mission and along with them a pool of Information Technology (IT) applications is functional under the digital health ecosystem. While some of these application cover institution level data but they did not record individualised data as well as they did not collect data on the source, hence leaving out opportunities around microplanning in healthcare.
To ensure timely availability of beneficiary wise data and to ensure tracking of women and children, there is a need for a digital data system that captures unitized data at source and enables interlinkages between different levels of health the system.
The Government of Uttar Pradesh (GoUP) aimed to develop a comprehensive data health system for the state, primarily for Frontline Workers (FLWs) such as ASHAs and ANMs. The data collected would be used by health officials to monitor, identify gaps, and develop implementation strategies. The system aims to reduce inequity by identifying and targeting left-out households and enabling effective tracking of women and children who miss services.
e-Kavach, a comprehensive digital health application (mobile and web-based), is a job aid for frontline workers and facility-based users that enables longitudinal tracking of patient information using a unique ID (ABHA ID).
Enumeration is the base module of the application which captures family as well as individual details of all family members within a household which is updated every six months by ASHA Worker. Once the ASHA has completed enumeration, enlisting all households and its members in her area, a list of target members (eligible couples, children) is automatically generated for service provision.
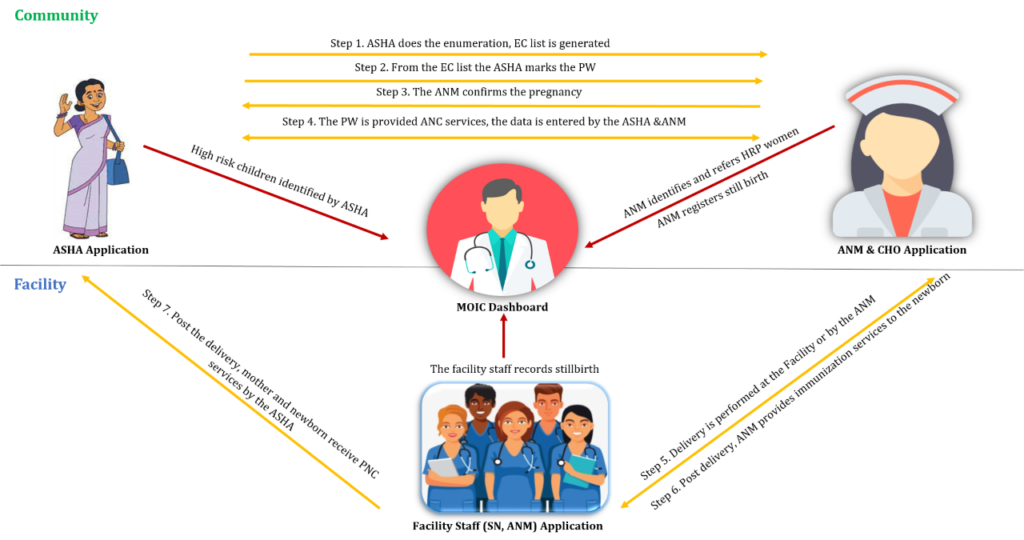
The ASHA, ANM and facility staff applications are interlinked, as depicted in Figure 1. Data entered into the application by any of the service providers will also be reflected in others’ applications. For example, a pregnant woman who is identified with a High-Risk Pregnancy (HRP) based on the examination and measurements conducted by the ANM, is reflected in the Medical Officer-In-Charge (MOIC)’s dashboard. The MOIC can then take necessary action for the treatment of the HRP woman.
Recognising the importance of digitalization of health data, the Government of Uttar Pradesh in consultation with the Government of India decided to pilot comprehensive digital health systems in the state. With the technical support from Uttar Pradesh Technical Support Unit (UP TSU), GoUP piloted the comprehensive digital health application – e-Kavach in Uttar Pradesh (UP) in July 2021.
UP TSU provided the following support to GoUP in rolling out the application:
(i) Identification customization of the application workflow.
(ii) Development of training material.
(iii) Implementation support for the pilot (including conducting trainings, providing handholding and helpdesk support).
The application has received a positive response from the FLWs. It eased their work and assisted them in performing their tasks in a streamlined manner. Nearly 33,399 households and 1,62,529 members were enumerated in the application by ASHAs within a month post enumeration training. Post RMNCH training, the FLWs initiated data entry into the RMNCH module of e-Kavach. Moreover, A total of 24,309 eligible couples, 2,504 children of age between 0-1 years and 1,276 pregnant women for ANC have been registered.
Learnings From the Pilot:
Based on the successful implementation of the pilot, the e-Kavach platform has been adopted by GoUP and is being scaled up across the state. UP TSU is providing necessary support to the GoUP during the scale up and is ensuring the application’s sustainability ensuring sustainability of the application.